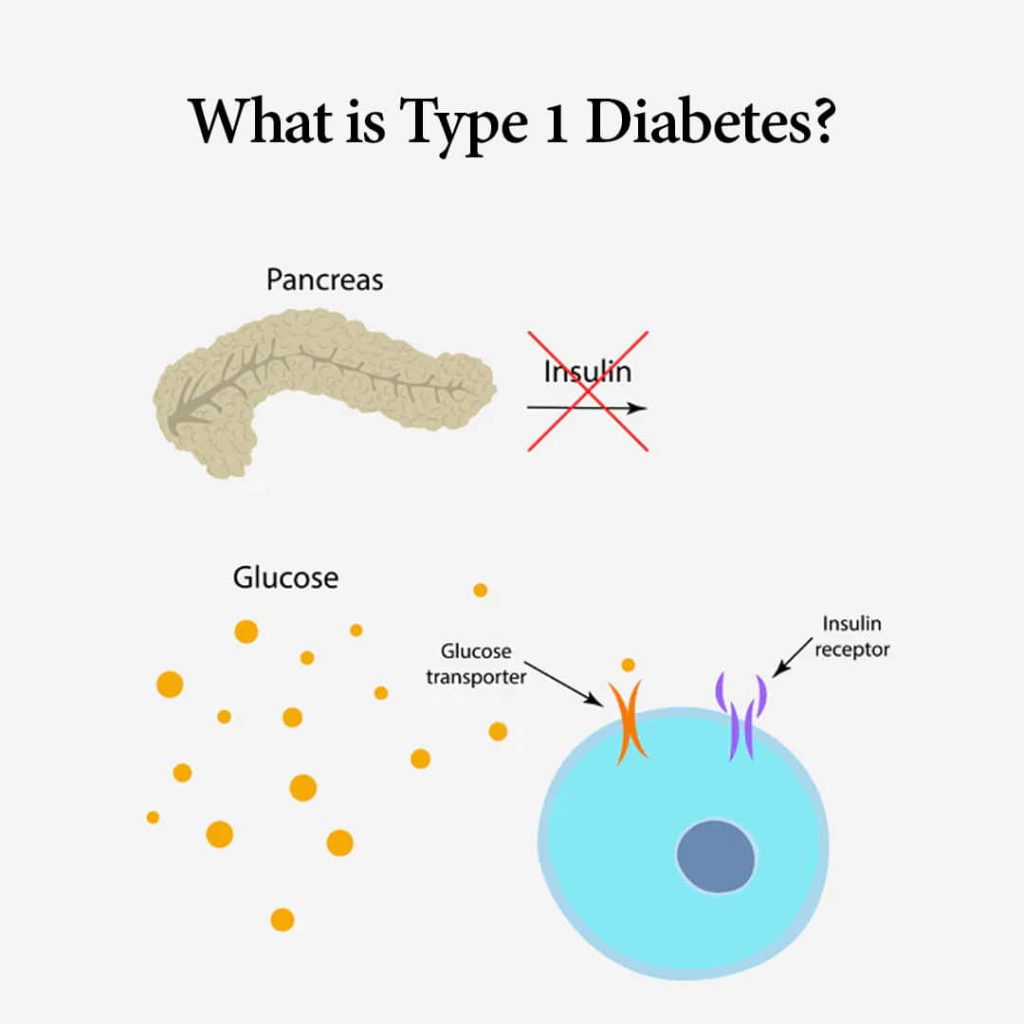
Type 1 diabetes is more than just a medical condition; it’s a way of life for millions around the globe. But what exactly is it? Unlike Type 2 diabetes, which is often associated with lifestyle factors, Type 1 diabetes is primarily an autoimmune disorder. This means the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks insulin-producing cells in the pancreas, leading to a lifelong need for insulin therapy.
Understanding the Basics
Type 1 diabetes is typically diagnosed in children and young adults, although it can appear at any age. It’s characterized by the body’s inability to produce insulin, a hormone crucial for converting glucose into energy. Without insulin, glucose builds up in the bloodstream, leading to high blood sugar levels.
Distinction from Type 2 Diabetes
While both Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes involve issues with insulin, they differ significantly in their causes and treatments. Type 2 diabetes usually occurs due to insulin resistance, where the body doesn’t use insulin effectively. It’s often linked to lifestyle factors such as obesity and inactivity. In contrast, Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune condition where the pancreas fails to produce insulin entirely.
Causes of Type 1 Diabetes
The exact cause of Type 1 diabetes remains a mystery, but several factors are believed to contribute to its development.
Genetic Factors
Genetics plays a significant role in the risk of developing Type 1 diabetes. Your chances of getting it are higher if you have a family history of the condition. However, the genetic link is complex and involves multiple genes, making it difficult to predict who will develop the disease.
Environmental Triggers
Environmental factors like viral infections are also thought to trigger Type 1 diabetes in genetically susceptible individuals. Some research suggests that exposure to certain viruses, such as the Coxsackievirus, can initiate the autoimmune process that destroys insulin-producing cells.
Autoimmune Response
In Type 1 diabetes, the immune system mistakenly attacks the beta cells in the pancreas. This autoimmune response is the primary cause of the disease, leading to the body’s inability to produce insulin. Scientists are still trying to understand why this response occurs, but it’s likely a combination of genetic predisposition and environmental triggers.
Symptoms of Type 1 Diabetes
Recognizing the symptoms of Type 1 diabetes early can make a significant difference in managing the condition effectively.
Early Warning Signs
Initial signs of Type 1 diabetes can be subtle and easily overlooked. These include frequent urination, excessive thirst, and unexplained weight loss. If you notice these symptoms, seeking medical advice promptly is crucial.
Common Symptoms
As the condition progresses, other symptoms, such as extreme fatigue, blurred vision, and increased hunger, may become more evident. These symptoms occur because the body isn’t getting the energy it needs from glucose due to the lack of insulin.
Severe Symptoms and Complications
In severe cases, if Type 1 diabetes is not managed correctly, it can lead to diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA). This is a dangerous condition where the body starts breaking down fat too quickly, leading to a build-up of acids in the blood. Symptoms of DKA include nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, and confusion, and it requires immediate medical attention.
Diagnosing Type 1 Diabetes
Accurate diagnosis is essential for the effective management of Type 1 diabetes. It involves several steps and tests.
Medical History and Physical Examination
The first step in diagnosing Type 1 diabetes is a thorough medical history and physical examination. Your healthcare provider will ask about your symptoms, family history, and recent illnesses.
Blood Tests
Blood tests are crucial for diagnosing diabetes. The primary tests include:
- Fasting Blood Sugar Test: Measures blood sugar after fasting overnight.
- A1C Test: Reflects average blood sugar levels over the past 2-3 months.
- Random Blood Sugar Test: This can be done anytime to check for high blood sugar levels.
Continuous Glucose Monitoring
Continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) can provide a more detailed picture of your blood sugar levels. CGMs provide real-time data on glucose levels and help identify patterns and trends in blood sugar fluctuations.
Managing Type 1 Diabetes
Living with Type 1 diabetes requires a multi-faceted approach to keep blood sugar levels within a target range.
Insulin Therapy
Since people with Type 1 diabetes can’t produce insulin, they need to take it externally. Insulin can be administered through injections or insulin pumps. Different types of insulin, ranging from rapid-acting to long-acting, are available to meet the body’s varying needs throughout the day.
Blood Sugar Monitoring
Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels is crucial. It helps adjust insulin doses, plan meals, and manage physical activity. Most people with Type 1 diabetes use blood glucose meters or CGMs to track their levels.
Lifestyle Modifications
Adopting a healthy lifestyle can significantly impact the management of Type 1 diabetes. This includes eating a balanced diet, engaging in regular physical activity, and avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption.
Diet and Nutrition for Type 1 Diabetics
Diet plays a crucial role in managing Type 1 diabetes. Knowing what to eat and how much to eat can help maintain blood sugar levels.
Importance of Carbohydrate Counting
Carbohydrates directly impact blood sugar levels. Counting carbs helps in planning meals and adjusting insulin doses accordingly. Understanding how different types of carbs affect blood sugar is essential for choosing healthier options.
Balanced Diet Recommendations
A balanced diet for someone with Type 1 diabetes should include a mix of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats. Whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats are recommended. Eating plenty of fruits and vegetables and avoiding processed and sugary foods is also essential.
Foods to Avoid
Certain foods can cause rapid spikes in blood sugar and should be limited or avoided. These include sugary snacks, refined carbohydrates, and high-fat, processed foods. Moderation is essential, and it’s always best to consult a dietitian for personalized advice.
Exercise and Physical Activity
Physical activity benefits everyone but is essential for managing Type 1 diabetes.
Benefits of Regular Exercise
Regular exercise helps improve insulin sensitivity, lowers blood sugar levels, and reduces the risk of complications. It also boosts overall health and well-being.
Tips for Safe Physical Activity
When you have Type 1 diabetes, planning your physical activity carefully is essential. Monitor your blood sugar levels before, during, and after exercise. Always have a source of fast-acting glucose on hand, such as juice or glucose tablets, to treat low blood sugar if needed.
Managing Blood Sugar During Exercise
Different types of exercise can affect blood sugar levels in various ways. Aerobic exercises may lower blood sugar levels, while anaerobic activities could cause spikes. Finding a balance and understanding how your body responds to different activities is essential.
Technological Advances in Diabetes Management
Technology has revolutionized how we manage Type 1 diabetes, making it easier and more effective.
Insulin Pumps
Insulin pumps provide a continuous supply of insulin throughout the day and night. They can be programmed to deliver different amounts of insulin based on your needs. Insulin pumps are especially useful for people with Type 1 diabetes who require precise control of their blood sugar levels.
Continuous Glucose Monitors (CGMs)
CGMs provide real-time glucose level feedback, helping prevent highs and lows. They are particularly beneficial for tracking trends and making informed insulin dosing and meal planning decisions.
Artificial Pancreas Systems
An artificial pancreas system combines an insulin pump with a CGM and an algorithm to adjust insulin delivery automatically. This system mimics the body’s natural insulin production and offers a promising solution for maintaining stable blood sugar levels.
Emotional and Psychological Impact
Managing Type 1 diabetes is not just a physical challenge; it also affects mental and emotional well-being.
Coping with a Chronic Condition
Living with Type 1 diabetes requires constant vigilance and can be overwhelming. It’s important to develop coping strategies and seek support when needed. This might include counseling, joining a support group, or talking to friends and family.
Support Systems and Resources
Having a solid support system can make a significant difference. Many resources, from online communities to diabetes educators, can provide valuable information and emotional support.
Mental Health and Diabetes
Diabetes can take a toll on mental health, leading to conditions like depression and anxiety. Regular check-ins with a mental health professional can help manage these challenges and improve overall well-being.
Type 1 Diabetes in Children
Type 1 diabetes presents unique challenges when diagnosed in childhood.
Diagnosis in Childhood
Children with Type 1 diabetes often face a different set of challenges than adults. Diagnosing and starting treatment early is crucial to prevent complications and ensure proper growth and development.
School and Social Challenges
Managing Type 1 diabetes in school can be challenging. It requires coordination with teachers, school nurses, and other staff to meet the child’s needs. Socially, children may feel different from their peers, and supporting them in navigating these experiences is essential.
Family Support and Education
Education and support for the whole family are vital in managing a child’s Type 1 diabetes. This includes learning about meal planning, insulin administration, and monitoring blood sugar levels.
Long-Term Complications
Even with careful management, Type 1 diabetes can lead to long-term complications over time.
Cardiovascular Disease
People with Type 1 diabetes are at a higher risk for cardiovascular diseases, such as heart attack and stroke. Managing blood sugar levels, maintaining a healthy diet, and regular exercise can help reduce this risk.
Kidney Damage (Nephropathy)
High blood sugar levels can damage the kidneys over time, leading to diabetic nephropathy. Regular monitoring of kidney function and maintaining healthy blood sugar levels are essential to prevent this complication.
Nerve Damage (Neuropathy)
Neuropathy, or nerve damage, is another common complication of Type 1 diabetes. It can cause symptoms like tingling, numbness, and pain, particularly in the hands and feet. Reasonable blood sugar control and regular check-ups can help prevent or manage this condition.
Preventive Measures and Risk Reduction
While Type 1 diabetes cannot be prevented, specific measures can help reduce the risk of complications.
Regular Monitoring and Check-ups
Frequent monitoring of blood sugar levels and regular medical check-ups are crucial. These help in early detection and management of potential complications.
Healthy Lifestyle Choices
Adopting a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet, regular exercise, and avoiding harmful habits like smoking, can significantly impact the overall management of Type 1 diabetes.
Vaccinations and Illness Prevention
People with Type 1 diabetes should stay up-to-date with vaccinations to prevent illnesses that could complicate their condition. Managing illnesses promptly and effectively is essential to avoid exacerbating blood sugar levels.
Type 1 Diabetes and Pregnancy
Pregnancy with Type 1 diabetes requires special care and planning.
Preconception Planning
Before becoming pregnant, women with Type 1 diabetes should work closely with their healthcare team to ensure optimal blood sugar control. This helps reduce the risk of complications for both mother and baby.
Managing Blood Sugar During Pregnancy
Blood sugar management becomes even more critical during pregnancy. It involves frequent monitoring and adjustments to insulin therapy to maintain stable blood sugar levels.
Postpartum Considerations
After giving birth, women with Type 1 diabetes need to continue managing their blood sugar levels carefully. This period can be challenging due to hormonal changes and the demands of caring for a newborn.
Current Research and Future Treatments
Research into Type 1 diabetes continues to advance, offering hope for new treatments and potential cures.
Advances in Treatment Options
Significant advancements have been made in treatment options, including new insulin formulations, improved insulin delivery systems, and better glucose monitoring technologies.
Potential for a Cure
Researchers are exploring various avenues for a potential cure, including pancreas transplants, stem cell therapies, and immunotherapy. While these are still experimental, they offer hope for the future.
Ongoing Clinical Trials
Many clinical trials are underway to test new treatments and therapies for Type 1 diabetes. Participating in these trials can provide access to cutting-edge treatments and contribute to advancing medical knowledge.
Conclusion and FAQs
Managing Type 1 diabetes is a lifelong journey that requires dedication and vigilance. With the right tools and support, individuals can lead healthy and fulfilling lives despite the challenges of this condition.
Practical Advice for Living with Type 1 Diabetes
- Stay Educated: Keep up-to-date with the latest information and research.
- Build a Support Network: Surround yourself with people who understand and support you.
- Embrace Technology: Utilize the latest tools and devices to manage your condition effectively.
- Prioritize Your Health: Regular check-ups and healthy lifestyle choices are essential.
- Stay Positive: Focus on what you can control and seek support when needed.
Frequently Asked Questions
- Can Type 1 diabetes be prevented?
No, Type 1 diabetes cannot be prevented. It is an autoimmune condition when the body’s immune system attacks insulin-producing cells in the pancreas.
- What is the difference between Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes?
Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disorder where the body cannot produce insulin, while Type 2 diabetes is characterized by insulin resistance and is often linked to lifestyle factors.
- How often should blood sugar levels be monitored?
Blood sugar levels should be monitored multiple times daily, especially before and after meals and during physical activity or illness.
- Can people with Type 1 diabetes lead everyday lives?
Yes, with proper management, people with Type 1 diabetes can lead healthy, active lives. It requires ongoing monitoring and treatment but does not prevent individuals from achieving their goals.
- Is there a cure for Type 1 diabetes?
Currently, there is no cure for Type 1 diabetes, but ongoing research and advances in treatment options continue to improve the quality of life for those affected by the condition.