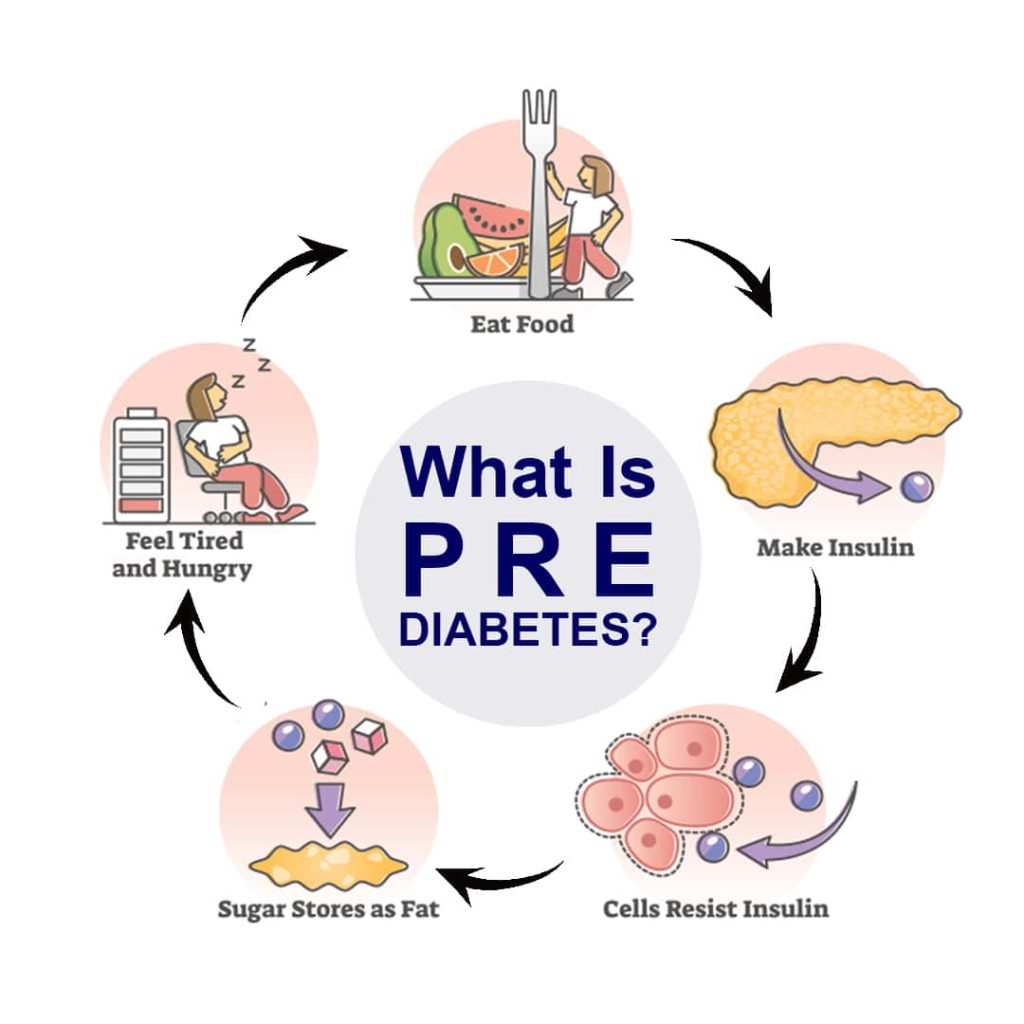
Prediabetes. It’s a term you might have heard tossed around in health circles, but what does it mean? Put, prediabetes is a condition where your blood sugar levels are higher than usual but not high enough to be classified as diabetes. Think of it as a warning signal—your body’s way of telling you that you’re on a risky path toward type 2 diabetes if you don’t make some changes.
Understanding prediabetes is crucial because it’s a silent precursor to more severe health issues. With millions of people worldwide affected, recognizing and addressing prediabetes can make a massive difference in your overall health and well-being. So, let’s dive into the nitty-gritty of what prediabetes is, why it happens, and how you can manage it effectively.
The Basics of Blood Sugar and Insulin
To manage prediabetes, you first need to understand how blood sugar and insulin work in your body.
How Blood Sugar Levels Work
Blood sugar, or glucose, is the primary type of sugar found in your blood. It comes from your food and is your body’s primary energy source. When you consume carbohydrates, your body breaks them down into glucose, entering your bloodstream.
But here’s the catch: too much glucose in your blood can be harmful. That’s where insulin comes in.
The Role of Insulin in Blood Sugar Regulation
Insulin is a hormone produced by your pancreas. Think of it as the key that unlocks your cells, allowing glucose to enter and be used for energy. Without enough insulin or if your cells become resistant to insulin’s effects, glucose stays in your bloodstream, leading to high blood sugar levels.
In the case of prediabetes, your body starts having trouble with insulin. Either it doesn’t produce enough insulin, or your cells become resistant to its effects. As a result, your blood sugar levels rise, setting the stage for diabetes if left unchecked.
Causes of Prediabetes
Prediabetes doesn’t just happen overnight. It’s usually the result of a combination of factors.
Genetic Factors
Your genes play a significant role in your risk of developing prediabetes. If you have a family history of diabetes, you’re more likely to develop prediabetes. Specific genes can affect how your body makes and uses insulin.
Lifestyle and Environmental Factors
While you can’t change your genes, you can control lifestyle factors. Poor diet, lack of physical activity, and being overweight are significant contributors to prediabetes. High-calorie, high-sugar diets and sedentary lifestyles can lead to weight gain and insulin resistance.
Symptoms of Prediabetes
One of the tricky things about prediabetes is that it often shows no apparent symptoms. However, there are some signs you should be aware of.
Early Warning Signs
Many people with prediabetes have no symptoms at all. However, some may notice darkened skin in certain body areas, such as the neck, armpits, and groin. This condition, called acanthosis nigricans, can be a sign of insulin resistance.
Common Symptoms to Watch Out For
Other symptoms to watch for include increased thirst, frequent urination, and unexplained weight loss. These symptoms are more common in diabetes but can occur in prediabetes as well.
Risk Factors for Prediabetes
Several factors can increase your risk of developing prediabetes.
Age and Family History
Your risk of prediabetes increases as you get older, especially after age 45. Having a family history of diabetes also raises your risk.
Weight and Physical Inactivity
Being overweight, mainly if you carry excess weight around your abdomen, is a significant risk factor. Physical inactivity compounds this risk, as regular exercise helps regulate blood sugar levels.
Other Contributing Factors
Other factors that can increase your risk include having high blood pressure, abnormal cholesterol levels, or polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS). Certain ethnicities, such as African American, Hispanic, Native American, and Asian American, are also at higher risk.
Diagnosing Prediabetes
Diagnosing prediabetes involves a few straightforward tests.
Types of Blood Tests
The most common tests used to diagnose prediabetes are:
- Fasting Blood Sugar Test: This measures blood sugar after an overnight fast. Levels between 100 and 125 mg/dL indicate prediabetes.
- Oral Glucose Tolerance Test (OGTT): This test measures your blood sugar before and two hours after you drink a sugary solution. Levels between 140-199 mg/dL after two hours indicate prediabetes.
- The hemoglobin A1c Test measures your average blood sugar levels over the past 2-3 months. A result between 5.7% and 6.4% suggests prediabetes.
Understanding Your Results
If your test results fall within the prediabetes range, it’s a wake-up call. You’re at a higher risk of developing type 2 diabetes and should take immediate steps to reverse this trend.
The Connection Between Prediabetes and Type 2 Diabetes
Understanding the link between prediabetes and diabetes is crucial for prevention.
How Prediabetes Can Lead to Diabetes
Prediabetes is essentially the halfway point to diabetes. Without intervention, many people with prediabetes will develop type 2 diabetes within 5-10 years. This happens because the underlying issues with insulin resistance or production worsen over time.
The Importance of Early Intervention
The good news is that early intervention can halt or even reverse the progression from prediabetes to diabetes. Lifestyle changes, such as improving your diet and increasing physical activity, are highly effective in preventing the onset of diabetes.
Health Risks Associated with Prediabetes
Prediabetes isn’t just about future diabetes risk. It also carries immediate health risks.
Cardiovascular Risks
People with prediabetes are at a higher risk of cardiovascular diseases, including heart attack and stroke. High blood sugar levels can damage blood vessels and nerves, contributing to these risks.
Other Potential Complications
Other complications of prediabetes include nerve damage (neuropathy), eye problems (retinopathy), and kidney damage. These issues are typically associated with diabetes but can begin in the prediabetic stage.
Preventing Prediabetes
The best way to deal with prediabetes is to prevent it in the first place.
Lifestyle Changes to Lower Risk
Small lifestyle changes can significantly lower your risk of developing prediabetes. Focus on eating a balanced diet, maintaining a healthy weight, and staying active.
The Role of Diet and Exercise
Diet and exercise are critical components of prevention. Aim to include more fruits, vegetables, and whole grains in your diet while reducing your sugary and processed foods intake. Regular physical activity helps improve insulin sensitivity and lowers blood sugar levels.
Managing Prediabetes
If you’ve been diagnosed with prediabetes, managing it is essential to prevent progression to diabetes.
Monitoring Your Blood Sugar
Keep an eye on your blood sugar levels through regular testing. This helps you understand how your body responds to different foods and activities.
Medications and Other Treatments
Sometimes, your doctor may recommend medications to help manage your blood sugar levels. These can include metformin, which helps reduce glucose production in the liver and improves insulin sensitivity.
Dietary Recommendations for Prediabetes
What you eat plays a huge role in managing prediabetes.
Foods to Include in Your Diet
Focus on incorporating fiber-rich foods like fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. Lean proteins and healthy fats, such as fish, nuts, and olive oil, are also beneficial.
Foods to Avoid
Limit your sugary foods and beverages, refined carbs, and processed foods. These can spike your blood sugar levels and contribute to insulin resistance.
Exercise and Prediabetes
Physical activity is a cornerstone of managing prediabetes.
The Benefits of Regular Physical Activity
Regular exercise helps your body use insulin more efficiently and can lower blood sugar levels. It also helps with weight management, which is crucial for reducing the risk of diabetes.
Types of Exercises to Consider
Aim for a mix of aerobic exercises (like walking, running, or cycling) and strength training. Even daily activities like gardening or taking the stairs can make a difference.
Stress Management and Its Impact on Prediabetes
Stress can have a significant impact on your blood sugar levels.
How Stress Affects Blood Sugar
When stressed, your body releases hormones like cortisol that can raise blood sugar levels. Chronic stress can lead to prolonged periods of high blood sugar, increasing the risk of prediabetes.
Techniques for Reducing Stress
Incorporate stress-reducing activities into your routine, such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, or hobbies you enjoy. Regular physical activity and good sleep hygiene also help manage stress levels.
Living with Prediabetes
Living with prediabetes involves making long-term changes to your lifestyle.
Creating a Support System
Having a support system can make managing prediabetes easier. This could include family, friends, or a healthcare team that can provide guidance and encouragement.
Long-Term Management Strategies
Focus on sustainable changes rather than quick fixes. This means adopting a balanced diet, staying active, managing stress, and keeping regular check-ups with your healthcare provider.
Conclusion
Prediabetes is a serious condition, but it’s not a sentence to develop diabetes. With the right approach, you can manage and even reverse prediabetes. Understanding the contributing factors, recognizing the signs, and making proactive changes can make a difference. Take charge of your health today and steer your life towards a healthier future.
FAQs About Prediabetes
- What is the Main Difference Between Prediabetes and Diabetes?
Prediabetes means your blood sugar levels are higher than usual but not high enough to be classified as diabetes. Diabetes, on the other hand, is when your blood sugar levels are consistently too high and require ongoing management. - Can Prediabetes Be Reversed?
Yes, prediabetes can often be reversed with lifestyle changes such as diet and exercise. The key is to take action early and make sustainable changes. - How Often Should I Get Tested for Prediabetes?
If you’re at risk for prediabetes, it’s recommended to get tested every 1-2 years. Your doctor can advise you on the best schedule based on your risk factors. - Is Medication Necessary for Managing Prediabetes?
Medication isn’t always necessary for managing prediabetes. Lifestyle changes are often sufficient. However, in some cases, doctors may prescribe medicines like metformin to help control blood sugar levels. - What Lifestyle Changes Can Make the Most Difference?
The most impactful lifestyle changes include eating a healthy, balanced diet, getting regular physical activity, managing stress, and maintaining a healthy weight. These changes can significantly lower your risk of progressing to diabetes.